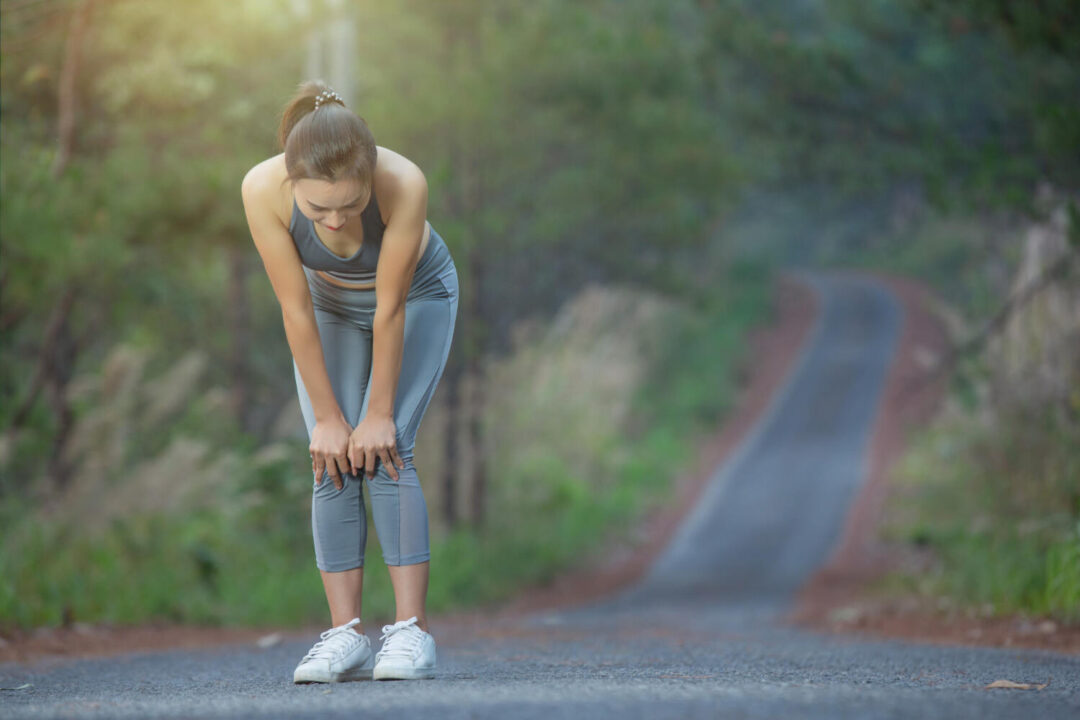
The Interconnection of Knee Pain and Back Pain
The relationship between back pain and knee pain is complex and influenced by numerous factors. These factors include medical conditions, posture, muscle strength, body mechanics, and anatomical considerations. Recent studies have shed light on the correlation between the intensity of knee pain and the levels of disability experienced by individuals with lower back pain. Understanding this relationship is crucial for effective management and treatment.
This comprehensive article explores the updated understanding of the intricate relationship between back pain and knee pain. It delves into the common causes of this association, provides insights into preventive measures, and outlines a range of treatment options available. By gaining a deeper understanding of this multifaceted connection, individuals can take proactive steps toward managing and alleviating both back and knee pain.
Can lower back pain cause knee pain?
Certainly, lower back pain can contribute to knee pain. The lower back, which is intricately connected to the knees through the pelvis and the sciatic nerve, plays a crucial role in maintaining overall musculoskeletal health. When the lower back is misaligned or experiences issues such as muscle imbalances or tightness, it can exert pressure on the sciatic nerve, leading to radiating pain down the legs and into the knees.
This tension and pressure on the sciatic nerve can result in inflammation, reduced range of motion, and discomfort in the knees. Moreover, a weak lower back may lead to compensatory overuse of the knees. When the lower back fails to provide adequate stability and support, the knees may bear more load and strain than they should, further exacerbating discomfort and potentially increasing the risk of knee injuries or chronic pain.
Therefore, it is important to address any issues or imbalances in the lower back to alleviate knee pain and promote overall musculoskeletal health. Engaging in exercises and techniques that focus on strengthening and stabilizing the lower back can help alleviate pressure on the sciatic nerve, reduce inflammation in the knees, improve range of motion, and promote proper alignment throughout the body.
Common Causes of Knee and Back Pain:
1. Overuse: Frequent bending, squatting, or kneeling, as well as improper form during physical activities, can strain joints and lead to inflammation.
2. Poor Posture: Unequal distribution of weight on the spine due to poor posture can result in muscle strain and tension, aggravated by prolonged sitting or repetitive motions.
3. Obesity: Excess weight places additional strain on joints and muscles, contributing to inflammation and pain.
4. Underlying Medical Conditions: Chronic knee and back pain may be caused by conditions such as arthritis, sciatica, or spinal stenosis, necessitating professional diagnosis and treatment.
How to Ease Back Pain:
For mild back pain, several home remedies can provide relief without medication or a doctor’s visit:
– Apply heat or cold to the affected area.
– Engage in low-impact exercises like walking, swimming, cycling, and yoga.
– Incorporate stretching routines targeting back, neck, and shoulder areas.
– Maintain proper posture to alleviate strain on muscles and reduce pain.
Best Treatment for Knee and Back Pain:
The optimal treatment depends on the underlying cause:
1. Physical therapy: Effective for improving flexibility, strengthening muscles, and reducing pain.
2. Pain medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and acetaminophen can help alleviate knee pain.
3. Spinal injections: Used to reduce inflammation and back pain.
4. Surgery: Considered in cases of structural issues or herniated discs.
Benefits of Having a Good Posture:
Maintaining good posture is crucial for preventing knee and back pain. By keeping your spine aligned properly, you can reduce the risk of experiencing back pain and improve your breathing. Moreover, maintaining good posture also contributes to better balance, improved circulation, reduced joint pain, and alleviation of pain and stiffness. Additionally, it can positively impact your digestion, increase your energy levels, and enhance your coordination. Taking care of your posture brings a multitude of benefits that can significantly improve your overall well-being.
Prevention Tips for Back and Knee Pain:
Besides practicing good posture, follow these updated prevention tips:
– Regular exercise to build muscle strength and flexibility.
– Maintain proper posture when sitting, standing, and lifting.
– Lift objects by bending your knees and keeping your back straight.
– Wear comfortable, supportive shoes.
– Take frequent breaks to avoid prolonged sitting or standing.
– Incorporate regular stretching into your daily routine.
– Consult your doctor about applying ice or heat for pain relief.
Conclusion
Understanding the intricate relationship between knee and back pain is crucial for effective prevention and management. By adopting these updated strategies and implementing a comprehensive approach to musculoskeletal health, individuals can promote overall well-being and significantly reduce the risk of discomfort in these common problem areas. Taking proactive measures such as maintaining proper posture, engaging in regular exercise that strengthens the core and surrounding muscles, and practicing mindful movements can all contribute to a healthier and pain-free lifestyle. It is important to prioritize self-care and seek professional guidance when needed, as a holistic approach to musculoskeletal health can greatly enhance quality of life and ensure long-term comfort and mobility.