The Interconnection of Knee Pain and Back Pain
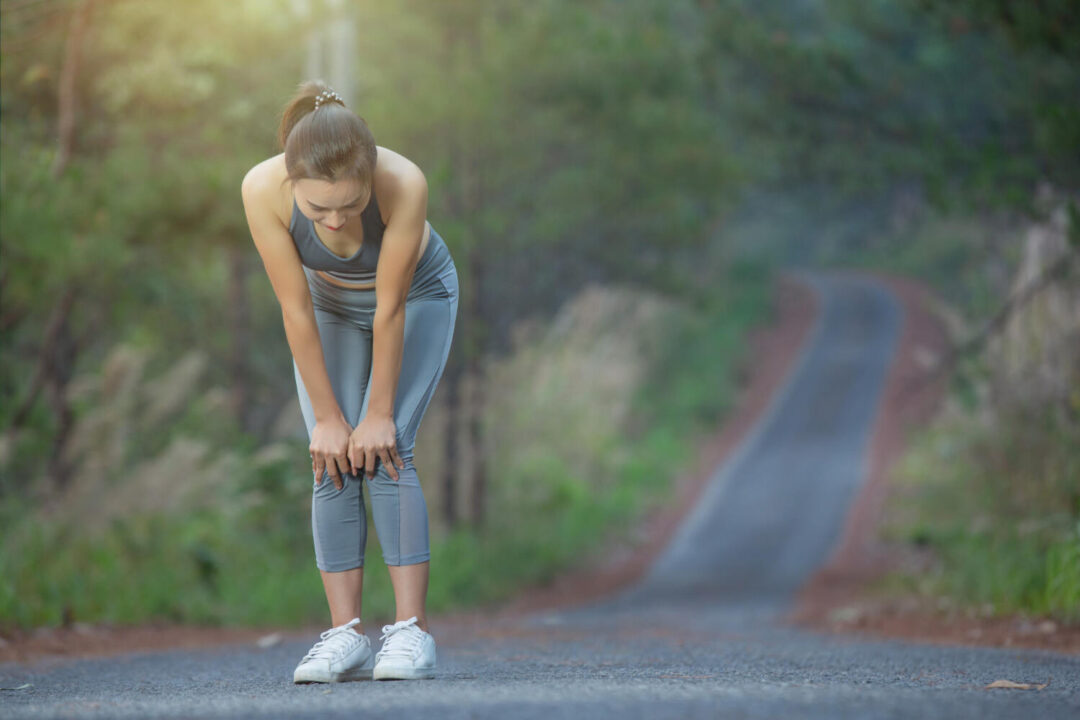
The relationship between back pain and knee pain is complex and influenced by numerous factors. These factors include medical conditions, posture, muscle strength, body mechanics, and anatomical considerations. Recent studies have shed light on the correlation between the intensity of knee pain and the levels of disability experienced by individuals with lower back pain. Understanding…